personality-tests
Big Five vs Enneagram: Which Framework is Better for Team Coaching and Leadership Development
Explore the strengths and weaknesses of the Big Five and Enneagram personality frameworks in the context of team coaching and leadership development.
Quick answer
Which personality framework is better for team coaching and leadership development?
For higher-stakes team and leadership decisions, Big Five is usually the stronger baseline because of its psychometric evidence. Enneagram is often useful as a reflection and communication layer.
Executive Summary
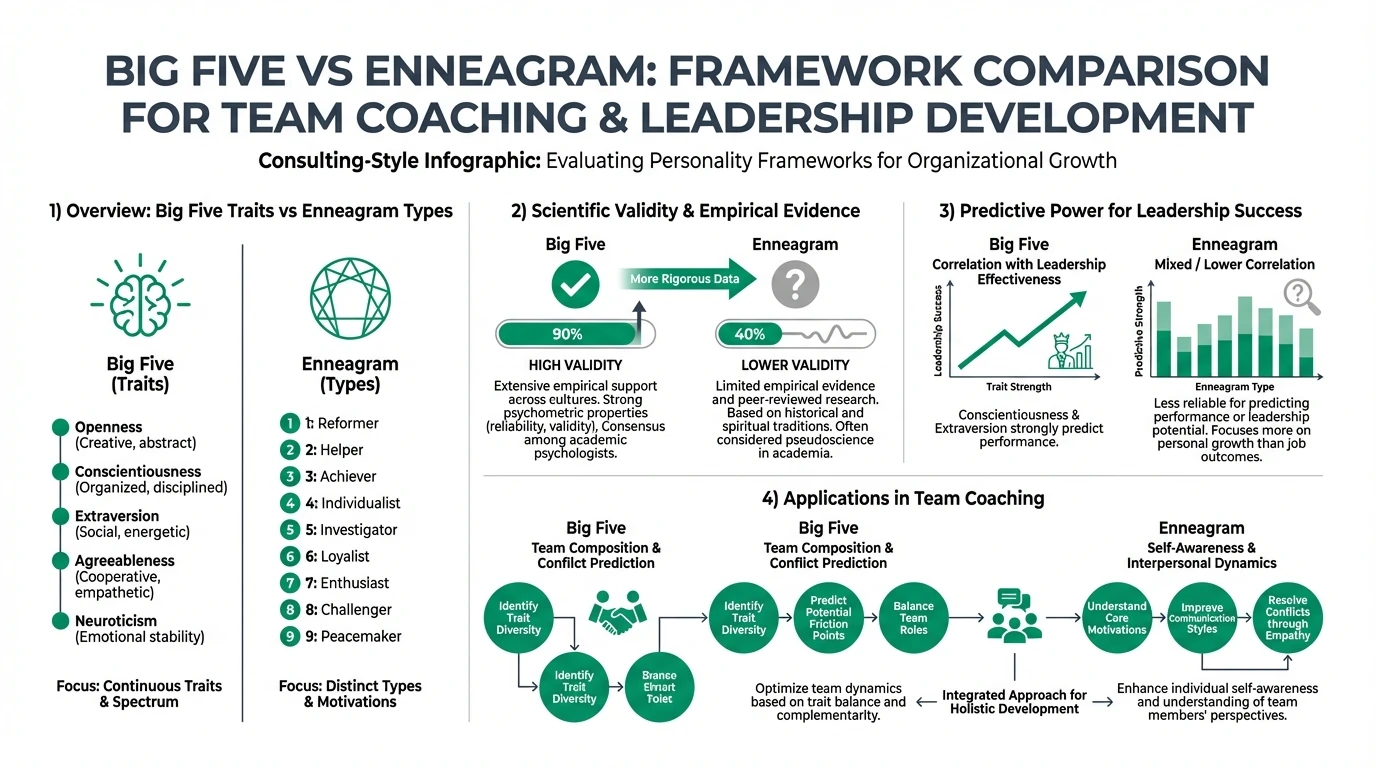
In the realm of team coaching and leadership development, the choice between the Big Five and Enneagram personality frameworks can significantly impact outcomes. The Big Five, also known as the Five-Factor Model, is renowned for its empirical validation and predictive power in professional settings. It assesses five broad traits—Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, and Neuroticism—making it a reliable tool for predicting behaviors and team dynamics123.
Conversely, the Enneagram categorizes personalities into nine types based on motivations and fears, providing qualitative insights into personal and relational development. While it lacks the scientific rigor of the Big Five, it excels in fostering self-awareness and interpersonal understanding123.
Key takeaway: The Big Five is preferred for its predictive validity in leadership and team performance, whereas the Enneagram is valued for enhancing self-awareness and relational dynamics.
If you need a trait-by-trait baseline before framework comparison, start with Big Five Personality Test: Complete Interpretation Guide. For methodological guardrails, keep Personality Test Reliability open while reviewing results.
Scientific Validity and Empirical Evidence
The Big Five framework is grounded in decades of psychological research, offering robust empirical evidence supporting its validity across various contexts. Its quantitative nature allows for precise measurement of personality traits, making it a staple in academic and professional settings123.
| Framework | Empirical Support | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Big Five | Strong | Recruitment, Team Building, Leadership Development |
| Enneagram | Limited | Personal Growth, Interpersonal Understanding |
For example, companies often use the Big Five to match employees with roles that align with their traits, enhancing job satisfaction and performance. You can operationalize this in workshops using the Big Five Role-Fit Calculator.
Predictive Power for Leadership Success and Team Performance
The predictive power of the Big Five is well-documented, with studies showing its effectiveness in forecasting job performance, team dynamics, and leadership success24. Its ability to quantify traits allows organizations to tailor development programs to individual needs.
In contrast, the Enneagram's focus on motivations offers insights into team dynamics by highlighting underlying fears and desires. However, its predictive accuracy is less reliable due to its qualitative nature.
Applications in Team Coaching: Trait-Based Matching vs. Motivation-Based Dynamics
In team coaching, the Big Five's trait-based approach facilitates precise matching of team members to roles, ensuring optimal team performance. This method is particularly effective in structured environments where specific traits are required for success12.
The Enneagram, on the other hand, enhances team dynamics by addressing motivational factors. It helps teams understand diverse perspectives, fostering empathy and collaboration.
| Approach | Focus | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Big Five | Traits | Role Fit, Performance |
| Enneagram | Motivations | Empathy, Collaboration |
For teams already using type-based language, MBTI vs Big Five is a useful bridge before introducing Enneagram use cases.
Strengths Mapping: Big Five's Quantitative Traits vs. Enneagram's Qualitative Growth Paths
The Big Five's quantitative nature allows for detailed strengths mapping, identifying areas for development and leveraging existing strengths. This approach is beneficial for creating targeted leadership development plans3.
The Enneagram provides a qualitative map of growth paths, guiding individuals through personal development journeys. While less precise, it encourages holistic growth by addressing core motivations and fears.
Integration Potential: Combining Both Frameworks for Comprehensive Development
Integrating the Big Five and Enneagram can offer a comprehensive approach to team coaching and leadership development. By leveraging the Big Five's predictive power and the Enneagram's motivational insights, organizations can create well-rounded development programs5.
For instance, a leader might use the Big Five to identify areas for skill enhancement while employing the Enneagram to foster emotional intelligence and relational skills.
Limitations in Professional Settings: Enneagram's Subjectivity vs. Big Five's Breadth
While the Big Five's broad applicability and empirical backing make it a reliable choice for professional settings, its lack of motivational insights can be a limitation. It describes behaviors without explaining the underlying "why"3.
The Enneagram's subjectivity and potential for mistyping pose challenges in professional environments. Its reliance on self-assessment can lead to inaccuracies, particularly in high-stakes settings3.
Cross-Cultural Reliability and Consistency in Diverse Teams
The Big Five's cross-cultural reliability is well-established, with validation across numerous cultures and studies3. This consistency makes it a preferred choice for global organizations seeking uniformity in personality assessment.
The Enneagram, while culturally rich, embeds philosophical assumptions that may not translate across diverse teams. Its subjective nature can lead to inconsistent results in multicultural environments.
Action checklist
- Evaluate team needs to determine the most suitable framework.
- Consider integrating both frameworks for a holistic approach.
- Ensure cultural considerations are accounted for in assessments.
FAQ
What is the primary difference between the Big Five and Enneagram?
Which framework is more scientifically validated?
Can the Enneagram be used for professional development?
How do the Big Five and Enneagram complement each other?
Is the Big Five applicable in cross-cultural contexts?
Primary Sources
| Source | Type | URL |
|---|---|---|
| APA Dictionary of Psychology | Institutional definition | dictionary.apa.org/five-factor-model |
| McCrae & John (1992) | Foundational Big Five paper | doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6494.1992.tb00970.x |
| Soto & John (2017), BFI-2 | Modern validation study | doi.org/10.1037/pspp0000092 |
| The Enneagram Institute | Enneagram model reference | enneagraminstitute.com |
| Clearer Thinking | Cross-framework outcome comparison | clearerthinking.org/post/how-accurate-are-popular-personality-test-frameworks-at-predicting-life-outcomes-a-detailed-investi |
Conclusion
For teams deciding between style-based and trait-based language, also compare DISC Personality Test: When to Use It vs Big Five before finalizing your coaching playbook.
Footnotes
-
APA Dictionary of Psychology, "Five-Factor Model." ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4
-
McCrae & John (1992), "An Introduction to the Five-Factor Model and Its Applications." ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4 ↩5
-
Soto & John (2017), "Short and Extra-Short Forms of the Big Five Inventory-2." ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4 ↩5 ↩6 ↩7
-
Clearer Thinking, "How Accurate Are Popular Personality Test Frameworks at Predicting Life Outcomes?" ↩
-
The Enneagram Institute, model overview and type descriptions. ↩